Copper Clad PCB
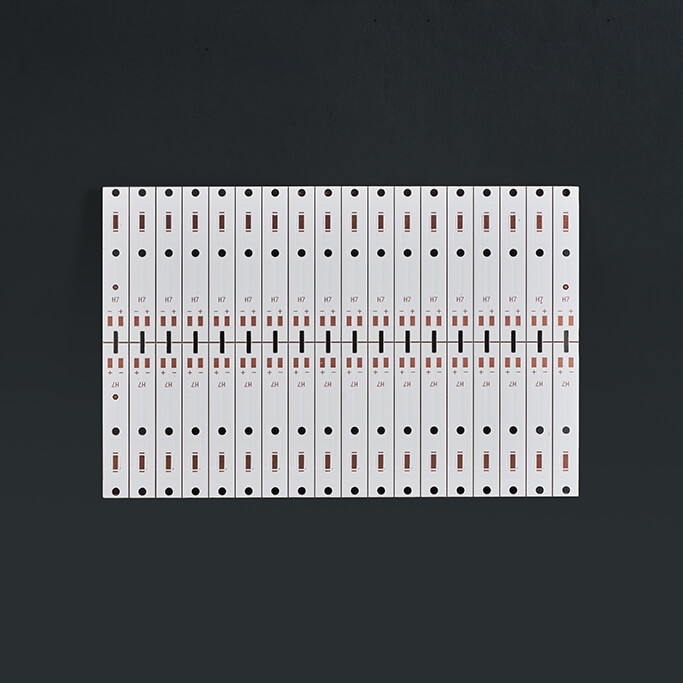





LEADHUI Copper PCB Overview
LEADHUI Copper PCB is a type of metal core printed circuit board (MCPCB) that features excellent thermal conductivity and mechanical stability. Unlike traditional FR4 or aluminum PCBs, copper-based boards provide superior heat dissipation and load-bearing capacity, making them ideal for high-performance applications.
Structure
The typical structure of a LEADHUI copper PCB includes:
- Circuit Layer (Copper Foil)
Conducts electricity and forms the electrical pathway. - Insulation Layer
A thermally conductive but electrically insulating layer that transfers heat from the circuit layer to the metal base. - Metal Base Layer (Copper Core)
Offers excellent thermal performance and mechanical strength, better than aluminum or steel substrates.
For more advanced applications, multi-layer copper PCBs can also be manufactured by laminating multiple circuit layers with insulating materials over a copper core.
Performance Features
- Superior Heat Dissipation
Copper has thermal conductivity of up to 398 W/m·K, far exceeding aluminum (~200 W/m·K) and FR4 (~0.3 W/m·K). - High Mechanical Strength
Ideal for applications with strong vibrations or mechanical stress. - Stable Dimensional Tolerance
Copper’s rigidity minimizes thermal expansion and improves long-term reliability. - Strong Current-Carrying Capacity
Supports high-current designs without overheating, suitable for power electronics.
Application Areas
LEADHUI Copper PCBs are widely used in industries where high heat and current loads are present, such as:
- High-power LED modules
- Power supply systems
- Electric vehicle (EV) chargers
- RF and microwave communications
- Solar panel controllers
- Motor control systems
- Automotive electronics
- Industrial automation
Advantages After PCB Fabrication
- Extended lifespan of components
Reduced heat stress on components leads to longer product life. - Improved circuit reliability
Stable performance even under high thermal cycles. - Compact design possibilities
High heat tolerance allows for smaller PCB sizes and tighter component layout. - Better EMI/EMC shielding
Copper’s high conductivity helps minimize electromagnetic interference.
