Aluminum Clad PCB
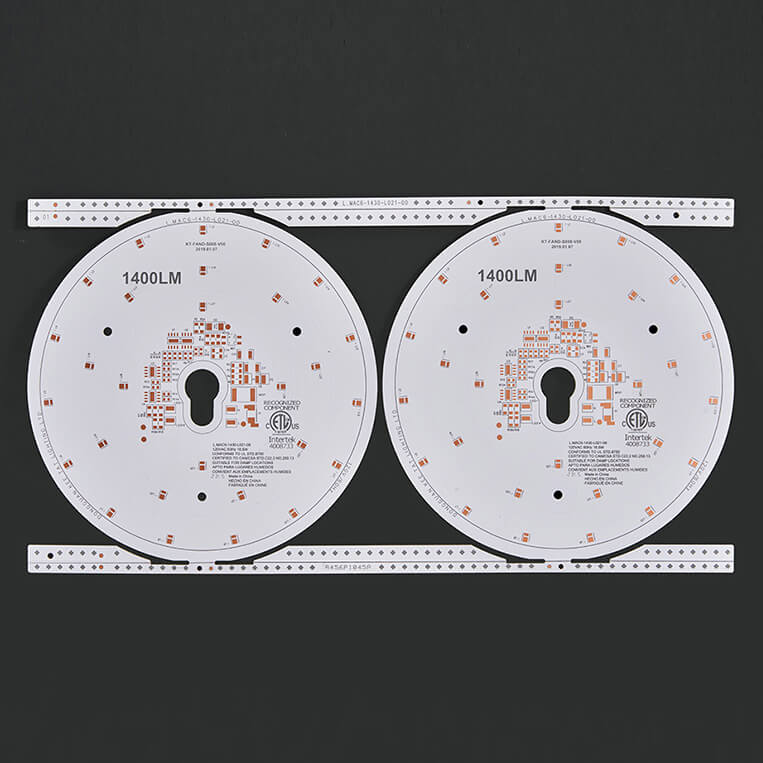
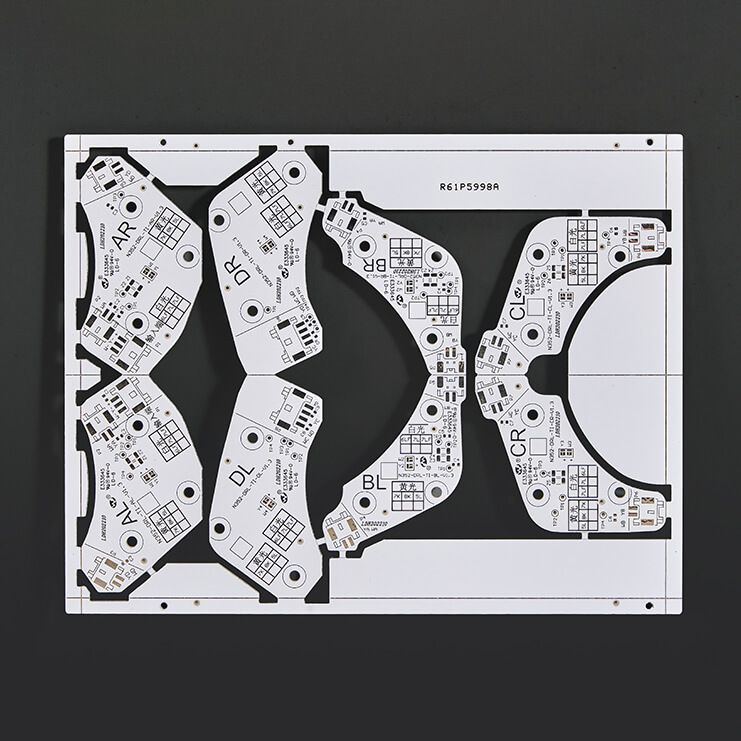




LEADHUI Aluminum PCB: Structure and Overview
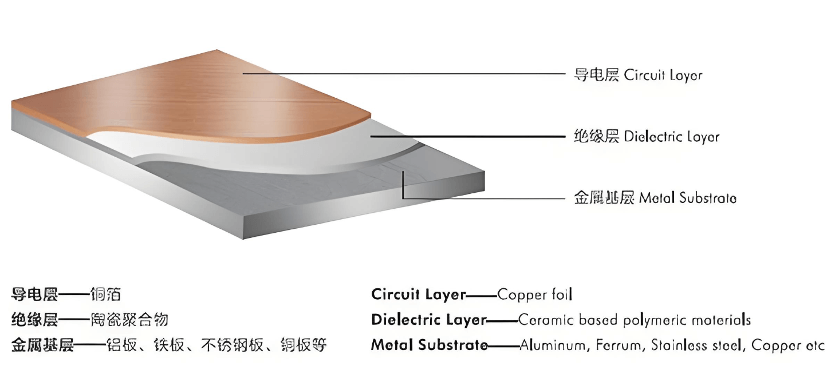
LEADHUI aluminum PCBs are metal-based copper-clad laminates with excellent heat dissipation properties. A typical single-sided board consists of three layers: the circuit layer (copper foil), the insulating layer, and the metal base layer.
For high-end applications, double-sided designs are also available, consisting of the structure: circuit layer – insulation layer – aluminum base – insulation layer – circuit layer. In rare cases, multilayer boards can be made by bonding standard multilayer PCBs with insulation and an aluminum base.
Advantages of LEADHUI Aluminum-Based PCBs
- Significantly better thermal dissipation compared to standard FR-4 structures.
- The dielectric used typically has 5 to 10 times the thermal conductivity of conventional epoxy glass, with only one-tenth the thickness.
- Heat transfer is more efficient than in traditional rigid PCBs.
- Allows the use of lower copper weights than those recommended in IPC standard diagrams.
Application Fields of LEADHUI Aluminum-Based PCBs
- Audio Equipment: Input/output amplifiers, balanced amplifiers, audio amplifiers, pre-amplifiers, power amplifiers, etc.
- Power Equipment: Switching regulators, DC/AC converters, SW regulators, etc.
- Communication Electronics: High-frequency amplifiers, filtering devices, transmitter circuits.
- Office Automation Equipment: Motor drivers, etc.
- Automotive Electronics: Electronic regulators, ignition devices, power controllers, etc.
- Computers: CPU boards, floppy drives, power supply units, etc.
- Power Modules: Inverters, solid-state relays, rectifier bridges, etc.
Aluminum-based PCBs are widely used in audio systems, power supplies, communication electronics, office automation, automobiles, computers, and power modules.
Design Requirements for LEADHUI Aluminum PCBs
Main technical requirements include:
- Dimensional specifications: board size and tolerance, thickness and tolerance, perpendicularity, and warpage.
- Appearance: Free of cracks, scratches, burrs, delamination, and aluminum oxidation stains.
- Performance: Requirements for peel strength, surface resistivity, breakdown voltage, dielectric constant, flammability, and thermal resistance.
Special testing methods for aluminum-based copper-clad laminates:
- Dielectric constant and dissipation factor: Measured by variable-Q series resonance method. The sample is connected in series with a tuning capacitor in a high-frequency circuit, and the Q value is measured.
- Thermal resistance: Calculated based on the temperature difference between measurement points and the corresponding heat transfer rate.
LEADHUI Aluminum PCB Manufacturing Process
(1) Mechanical Processing:
Drilling aluminum PCBs is possible, but no burrs are allowed on the edges of the holes, as this affects high-voltage testing. Milling the outline is extremely challenging. Punching requires high-end molds with precise craftsmanship, which is one of the key difficulties in aluminum PCB manufacturing.
After punching the board, the edges must be neat and burr-free, and the solder mask on the board edges must not be damaged. Typically, compound molds are used: holes are punched from the circuit side, outlines from the aluminum side. Techniques such as upper shear and lower pull are employed. After punching, the board warpage must be less than 0.5%.
(2) Aluminum Base Surface Protection:
Throughout the production process, the aluminum surface must not be scratched or touched. Hand contact or exposure to chemicals can cause discoloration or blackening, which is unacceptable. Some customers also do not accept re-polished aluminum surfaces. Avoiding any contact with the aluminum surface throughout the entire process is a key challenge.
Some companies apply a passivation treatment, while others use protective films before and after hot air solder leveling (HASL). Various creative techniques are used to solve this challenge.
(3) High-Voltage Testing:
Communication power aluminum PCBs require 100% high-voltage testing. Some clients require DC testing, others AC, with voltages of 1500V or 1600V for 5–10 seconds. Every single board must be tested. Any surface contamination, hole or aluminum edge burrs, jagged traces, or damage to the insulation layer can cause arcing, leakage, or breakdown during testing. Boards that delaminate or bubble during testing will be rejected.
LEADHUI Aluminum PCB Manufacturing Specifications
- Aluminum PCBs are often used in power devices with high power density, requiring thicker copper foil. If copper thickness exceeds 3 oz, etching compensation in design is needed; otherwise, the line width will be out of tolerance after etching.
- The aluminum surface must be protected with a film before PCB processing. Exposure to chemicals can corrode the surface and affect appearance. Since the film can be easily damaged, the boards must be placed in protective frames throughout the process.
- The milling bits used for fiberglass PCBs have lower hardness, while those for aluminum PCBs must be harder. Milling aluminum is at least two-thirds slower than milling fiberglass.
- When milling fiberglass PCBs, the machine’s built-in cooling is sufficient. But for aluminum PCBs, additional alcohol cooling must be applied directly to the router bit.
